Signed Heat Method (Python)
signedheat3d is a Python library implementing the Signed Heat Method for computing robust signed distance fields (SDFs) to triangle meshes, polygon meshes, and point clouds in 3D.
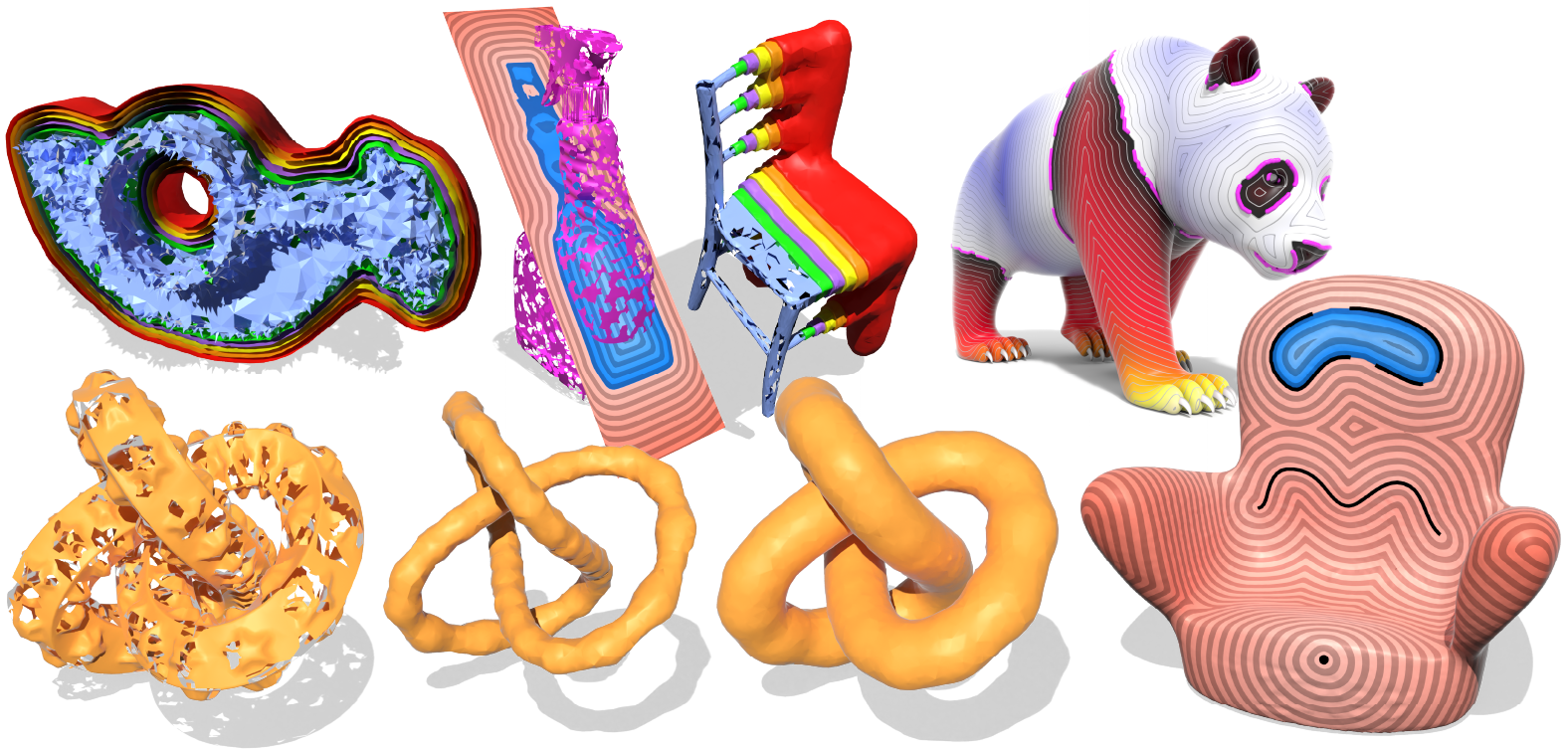
This library consists of Python bindings to C++ code. Toggle the “C++/Python” switch at the top of this page to see documentation for the C++ version.
Install signedheat3d via PyPI:
Sample:
import signedheat3d as shm
V, F = # your mesh, specified as a vertex and face array
# Initalize tet mesh solver
tet_solver = shm.SignedHeatTetSolver(verbose=True) # print all messages
# Solve!
sdf_tets = tet_solver.compute_distance_to_mesh(V, F)
# Solve on a regular grid instead.
grid_solver = shm.SignedHeatGridSolver(verbose=True)
sdf_grid = grid_solver.compute_distance_to_mesh(V, F)
For a demo, see the sample project, which uses Polyscope for visualization.
More info about the method, including a blog-style summary, an introductory 10-minute talk, and the corresponding academic paper are all located at the project page here.
Related libraries
The Signed Heat Method has been implemented in both C++ and Python, in 2D and in 3D.
- If you’re interested in using the Signed Heat Method on 2D surface domains, rather than in 3D space, the method has been implemented in geometry-central for triangle mesh domains, polygon mesh domains, and point cloud domains. A demo project exists at signed-heat-demo.
- Likewise, Python bindings to the geometry-central C++ code has been implemented in the Python package potpourri3d.
Credits
signedheat3d is developed by Nicole Feng, with advice from Alex Kaszynski and Nicholas Sharp.
If this code contributes to an academic publication, cite it as:
@article{Feng:2024:SHM,
author = {Feng, Nicole and Crane, Keenan},
title = {A Heat Method for Generalized Signed Distance},
year = {2024},
issue_date = {August 2024},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
volume = {43},
number = {4},
issn = {0730-0301},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3658220},
doi = {10.1145/3658220},
journal = {ACM Trans. Graph.},
month = {jul},
articleno = {92},
numpages = {16}
}